Map Editor Overview†
The map editor is the main tool in game creation, creating the terrain and buildings where the game will take place and placing events related to the storyline.
The structure and functions of the map editor are as follows.
1) Editor Screen†
This is the main work screen of the Map Editor, where you change the form of the terrain and place objects and events.
The working camera can be rotated by right dragging.
Center-drag or hold down the Shift key and right-drag to scroll in the X-axis and Z-axis directions.
Zoom in/out by rotating the wheel.
- 3D Display Icons
This icon appears in the upper left corner of the editor screen.
- Clicking on each of the X, Y, and Z cubes will give you a viewpoint from each axis.
- Left click to turn on/off perspective
- Click on the icon in the upper left corner of the preview screen to open the "Editor Settings" tab of the "Map Settings" palette.
- Map Symbols
The following map symbols will be placed on maps when events, lights, etc. are placed.
The display of the map symbols can be toggled on and off using the buttons at (4), the bottom of the Map Editor.
| Icon | Description |
|
| Indicates the starting point of the game. |
|
| Represents an event for which no graphics are specified. |
|
| Represents a particle. |
|
| Represents a local light (point light). It can be moved and scaled. |
|
| Represents a local light (spotlight). It can be moved, rotated, and scaled. |
|
| Represents a decal. It can be moved, rotated, and scaled. |
|
| Represents the destination of an event involving a location move. Moving this symbol will be reflected in the content of the event. |
|
| This represents the frames of camera work belonging to this map created by the Camera Tool for which the gazing point is specified in the world. When this symbol is moved or rotated, it is also reflected in the camera data. |
Context Menu†
If you right-click while selecting something on the map, a context menu will appear.
The context menu that appears changes depending on whether terrain, object, or event is selected.
- Selecting Terrain
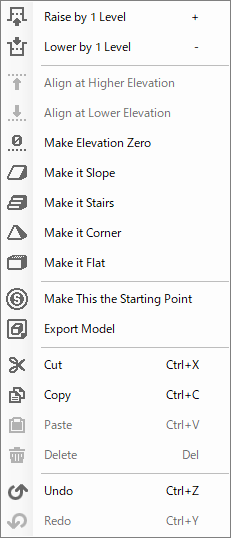
| Raise by 1 Level | Raise the Y-coordinate of the currently selected terrain by one step (0.25). |
| Lower by 1 Level | Lower the Y-coordinate of the currently selected terrain by one step (0.25). |
| Align at Higher Elevation | If you have selected terrain of different elevations, align the Y-coordinate plane to the higher one. |
| Align at Lower Elevation | If you have selected terrain of different elevations, align the Y-coordinate plane to the lower one. |
| Make Elevation Zero | Set the elevation of the currently selected terrain to the lowest (Y=0.25). |
| Make it Slope | Convert terrain with steps to a slope with the assigned orientation. Used on terrain with higher steps.
Multiple adjacent terrains can be selected to make a slope. Slopes can only be connected by up to 4 levels of elevation difference. |
| Make it Stairs | Convert terrain with steps to a slope with the assigned orientation. Used on terrain with higher steps.
Multiple adjacent terrains can be selected to make stairs. Stairs can be connected by up to four different elevation levels. |
| Make it Corner | It is a function that makes the two adjacent sides of the terrain a slope or stairs, and the break in the terrain is also a slope or stairs.
The elevation of the terrain to be angled should be the same as that of the slope or stairs. |
| Make it Flat | Sloping terrain such as "Make it Slope" and "Make it Stairs" will be undone. |
| Make This the Starting Point | Specify the selected point as the position of the main cast member at the beginning of the game. |
| Export Model | Export the currently selected terrain as a 3D model (.fbx). |
| Cut | Cut the currently selected terrain. |
| Copy | Copy the currently selected terrain. |
| Paste | Paste the copied terrain. |
| Delete | (Terrain cannot be deleted.) |
| Undo | Undo the operation. |
| Redo | Redo the operation. |
- Model Export of Terrain
This function allows you to export the currently selected terrain as model data in FBX format.
By successfully combining 3D modeled terrain, it is also possible to represent terrain with holes in it, for example.
- When exporting, all areas above "elevation 0" are exported.
- If you want your exported model to look the same as the terrain when imported into Bakin, go to Resources > Materials and assign "map_terrain" to Shader.
- Add Bottom Surface
If checked, the export will be done with the bottom side attached.
- Contain Map Objects
If checked, the export will include objects on the selected terrain.
The following restrictions apply to objects:
- Collisions are not fully reproduced.
- Motions will not be reproduced.
- The materials will be the fbx defaults.
- Create the Collision File
When exporting, collision files are generated at the same time.
- Normal Dividing Boundary (Degree)
- Selecting Objects
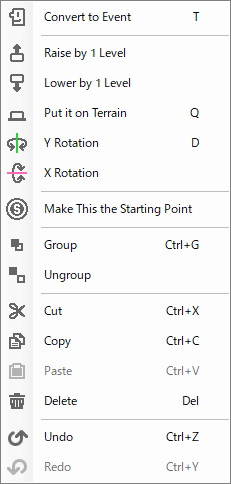
| Convert to Event | Convert the selected object to an event. |
| Raise by 1 Level | Raise the Y-coordinate of the currently selected objects/events by one step (0.25). |
| Lower by 1 Level | Lower the Y-coordinate of the currently selected objects/events by one step (0.25). |
| Put it on Terrain | Place the objects/events floating in the air on the ground. |
| Y Rotation | Rotate the selected objects/events by 45 degrees around the Y axis. |
| X Rotation | Rotate the selected objects/events 45 degrees around the X axis. |
| Make This the Starting Point | Specify the selected point as the position of the main cast member at the beginning of the game. |
| Group | Group multiple selected objects/events.
All grouped objects/events can be repositioned, resized, etc. at the same time. |
| Ungroup | Ungrouping is performed by selecting any object in the group. Any object in the group can be selected for ungrouping. |
| Cut | Cut the currently selected objects. |
| Copy | Copy the currently selected objects. |
| Paste | Paste the copied objects. |
| Delete | Delete the currently selected objects. |
| Undo | Undo the operation. |
| Redo | Redo the operation. |
- Selecting Events
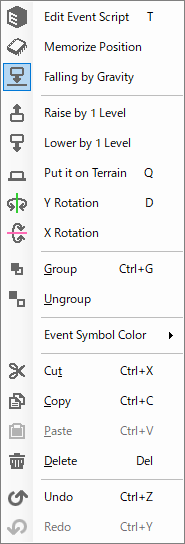
| Edit Event Script | Open the Event Editor. |
| Memorize Position | If turned on, this event will retain its post-movement position even if the player moves to another map after using a movement-based event to change this event's position on the map. |
| Falling by Gravity | If turned on, that event will fall by gravity when play begins.
When turned off, it maintains the Y-axis position and events that are suspended in mid-air remain suspended in mid-air.
This setting affects the behavior of movement events and other events. |
| Raise by 1 Level | Raise the Y-coordinate of the currently selected objects/events by one step (0.25). |
| Lower by 1 Level | Lower the Y-coordinate of the currently selected objects/events by one step (0.25). |
| Put it on Terrain | Place the objects/events floating in the air on the ground. |
| Y Rotation | Rotate the selected objects/events by 45 degrees around the Y axis. |
| X Rotation | Rotate the selected objects/events 45 degrees around the X axis. |
| Make This the Starting Point | Specify the selected point as the position of the main cast member at the beginning of the game. |
| Group | Group multiple selected objects/events.
All grouped objects/events can be repositioned, resized, etc. at the same time. |
| Ungroup | Ungrouping is performed by selecting any object in the group. Any object in the group can be selected for ungrouping. |
| Event Symbol Color | You can specify the color of the "event symbols" that represent events that do not have graphics assigned to them in the Map Editor. |
| Cut | Cut the currently selected events. |
| Copy | Copy the currently selected events. |
| Paste | Paste the copied events. |
| Delete | Delete the currently selected events. |
| Undo | Undo the operation. |
| Redo | Redo the operation. |
- Event Symbol Color
This feature allows you to color "event symbols" that represent events that do not have graphics assigned to them in the Map Editor.
Eight colors are available.
For example, "red for camera control events" and "white for off-map movement events" can be used to classify events by type.
2) Master Menu†
This menu provides access to the main features of Bakin.
Clicking on each menu opens the respective dialog.
For details on each menu, see the page for each menu in the manual.
3) Menu Bar†
The menu bar at the top of the Map Editor window provides access to various features.
- Save
Overwrite and save the game data currently being worked on.
- Undo
Undo the previous operation and return to the original state.
Multiple operations can be undone by continuing to click.
- Redo
Restore an operation that was undone with "Undo".
If there are multiple undone operations, you can go back to them by continuing to click.
- File
- Save
Overwrite and save the game data currently being worked on.
- Save as New Project Name
Save the game data you are currently working with under a different name.
- Version
The version information of this software is displayed.
- Utilities/Export
A diagram will open to export the publish work (exe file).
- Return to Top Menu
Close the game data you are currently working with and return to the top menu.
- Edit
- Undo
Undo the previous operation and return to the original state.
Multiple operations can be undone by continuing to click.
- Redo
Restore an operation that was undone with "Undo".
If there are multiple undone operations, you can go back to them by continuing to click.
- Cut
Cut out the selected objects or events and copy them to the clipboard.
- Copy
Copy the selected objects or events to the clipboard.
- Paste
Paste copied objects or events to the clipboard.
"Cut", "Copy", and "Paste" change behavior depending on the mode of the selection in the status bar at the bottom of the map editor.
- "Terrains Only": Copy, cut, and paste selected terrains.
- "Objects Only": Copy, cut, and paste selected objects and events.
- "Terrains and Objects": Copy, cut, and paste selected terrains and the objects/events that will be placed on them.
- Delete
Delete the selected objects or events.
- Alignment
- Position
Align multiple selected objects or events with the same X, Y, and Z coordinates as the first one selected.
If ALL is selected, they are all placed on the same coordinates.
- Rotation
Align multiple selected objects or events with the same X, Y, and Z axis angles as the first one selected.
If ALL is selected, all the angles will be the same.
- Scale
Align multiple selected objects or events with the same X, Y, and Z axis scales as the first one selected.
If ALL is selected, all will be on the same scale.
- Scroll Entire Map
The entire map currently being edited can be shifted one level at a time in the specified direction.
Each time you click on an arrow on the diagram, it will shift in that direction.
The area that is out of the map area will disappear, but if you check the "Treat as Loop" checkbox, the area that has shifted and disappeared from the map area will appear from the opposite direction.
However, if "Treat as Loop" is on, the position of objects placed outside the map area will not change.
You can also rotate the map 90 degrees by clicking the left and right curved arrow buttons.
- Raise Up Entire Map
Raise the elevation of the entire map's terrain by one level.
- Lower Down Entire Map
Lower the elevation of the entire map's terrain by one level.
- Adjust Elevation of Entire Map
Change the elevation of the entire map. Enter a negative (minus) value to make it lower than the current elevation, or a positive value to make it higher.
- Specify Entire Map as Elevation 1
Make the map a flat terrain with an elevation of 1.
- Delete Unused Files in Resource Folder
Locate and delete files in the resource folder that are not used for the game.
It is used when exporting a publishing work.
- Clear File Paths
Remove all paths that refer to anything other than within the game file.
It is used when exporting a publishing work.
- View
- Snap to Grid
Enable/disable the Grid Snap function, which positions objects and events along grids.
- Show Grids
Show/hide the grids on the map.
- Show Enemy Distribution
Show/hide areas where enemies appear.
- View with Perspective
Switch between having the map you are working on displayed with/without perspective.
- Post-Effects Enable
Switch between applying or not applying the post-effects specified for the map you are working on.
- Camera from Above
When turned on, the camera will look at the viewpoint from directly above. Turn off to return to the previous viewpoint.
- DOF Enable
Enable/disable the DOF (depth of field) function.
- View Project Paths
Display/hide the project path shown in the upper right of the Map Editor.
This can be used when you do not want to show the path when broadcasting a work scene.
- Quick Toolbar
Display/hide the Quick Toolbar.
- Various Palettes
Show/hide various palettes.
Hidden palettes will not be visible from the storage areas on the left and right sides of the preview screen.
- Window Initialization
Initialize the size of the Map Editor window.
- Palette Initialization
Initialize the position and separation state of various pallets.
- Delete All Error Thumbnails
Delete all thumbnails that failed to be created and are displayed in error.
For example, if a 3D stamp model file that has already been imported is deleted from the project folder using Windows Explorer, the thumbnail of that stamp or model will change to an error thumbnail in various places in the tool.
Use this function when the error thumbnail does not disappear even after the deleted model is put back into the project folder.
- Delete All Thumbnails
Delete all thumbnails generated by each function.
Thumbnails are newly generated when the game file is loaded.
- Functions
You can access each function in the master menu.
You can also use extensions (plug-ins).
- Copy Battle-Related Scripts to Game File (Default Battle)
Export the Bakin default battle-related sources to the battlescript folder in your project.
- Copy Battle-Related Scripts to Game File (Battle Plug-in Sample)
Export the battle-related sources from the "Battle Plug-in Sample" project in the Game Gallery to the battlescript folder in your project.
- Remove Battle-Related Scripts from Game File
Delete the battlescript folder and revert to the default battle process.
- Configuration
This opens a dialog where you can set the folder where the project will be saved, set the behavior of the Map Editor tools, customize shortcut keys, etc.
- "General" Menu
You can use this dialog to configure various settings found in the Top Menu > Configuration.
General > Language can be reflected by restarting Bakin.
- "Shortcuts" Menu
You can customize the shortcut key settings that can be used when operating the tool.
The assignment can be changed by clicking on the middle column of the three columns and typing the key you wish to assign from the keyboard.
- Help
You will find links to the web page below.
Clicking on each link will open the page accordingly in your browser:
"RPG Developer Bakin Manual", "Shortcut Key List", "Official Website", "YouTube Official Video", "Update Log" and "Contact us".
From "Contact us" you can open the contact page of the official website with your browser.
- Version Information
This is the version number of the tool.
Left-clicking copies the version number.
(Please include the version number when contacting us in case of trouble.)
- Path Information
Shows the path where the game file currently being edited is saved.
Right-click to open the folder where the game file is stored in Explorer.
You can also save your project in a Zip file.
When compiling into a Zip file, it is possible to remove the import paths for the resources in the project.
Please use this function if you need it to distribute your project.
Test Play†
You can execute the game player feature to test play the game in its current state.
There are two buttons to start the test play.
- The left button (the button with the green triangle) changes its behavior depending on how it is clicked.
- Left Click: Quick Test Play. The editor is not available during test play.
- Right Click: Skip the title screen for a quick test play.
- Center Wheel Click: Test Play. Test play is performed in a separate process from the editor. You can use the editor during the test play. The test play will be the same environment as when the project is exported as a published work.
- The right button (the button with the ... symbol) has a function that allows you to select saved data and execute a test play.
All features and notations described below are defaults.
The assignment of keys and buttons to be used can be changed in Assign Input Device.
- Title Screen Menu
- New Game
Play from the beginning of the game.
- Continue
Play the saved game from the continuation.
- Config
Specify various settings for the game. You can also do this in-game.
- BGM
Specify the volume of the background music.
- Sound Effects
Specify the volume of sound effects.
- Message Speed
Select from four levels of message display speed.
- Cursor Position
Specify whether the cursor position is to be memorized or not.
- Restore Defaults
Restore the configuration settings to their default values.
- Exit Game
Exit the test play and return to the map editor.
Keyboard Operation†
Cursor Control
Player Movement | Cursor keys, ADWS keys |
|---|
| Run | Shift+Movement Operation |
|---|
| Jump | X key |
|---|
| Menu Display | Enter key, ESC key, M key |
|---|
| Decision | Enter key, Space key, Z key |
|---|
| Cancel | ESC key |
|---|
| Speak and Investigate | Space key, Z key |
|---|
| Horizontal Camera Rotation | EQ key |
|---|
| Vertical Camera Rotation | RF key |
|---|
| Zoom in/out | TG key |
|---|
| Reset Camera Position | P key |
|---|
| Return to the Title Screen | Ctrl + C key |
|---|
| Fast-Forward Event/Camera | LeftCtrl |
|---|
| Open/Close the Debug Window | F5 Key |
|---|
| Open/Close the Cast Parameter Check View | F6 Key |
|---|
| Immediate End of Game | Alt+F4 Key |
|---|
Controller Operation†
Cursor Control
Player Movement | Direction buttons, left stick |
|---|
| Run | X Button + Movement Operation |
|---|
| Jump | Y Button |
|---|
| Menu Display | START Button |
|---|
| Decision | B Button |
|---|
| Cancel | A Button |
|---|
| Speak and Investigate | B Button |
|---|
| Horizontal Camera Rotation | Right stick left/right |
|---|
| Vertical Camera Rotation | Right stick up/down |
|---|
| Zoom in | LB + RB Button |
|---|
| Zoom out | LB + RT Button |
|---|
| Reset Camera Position | Press in the right stick |
|---|
Options†
You can choose from a variety of menus that allow you to change and check the behavior while executing test plays.
This menu is not selectable during test play with center wheel click.
- Window Size
You can change the size of the window during test play.
- Performance Meter
You can check how much load is placed on each element in the game.
- Debug Window
You can change/check the state of variables in the game and specify during battles.
- Cast Parameter Check View
You can check or temporarily change the statuses and parameters of the casts in the game.
- View Collision
Visually check the collision specified for objects and events.
Please use this function to help you find errors in collision setup, etc.
About the Debug Window†
Pressing the "F5 key" during test play opens and closes the Debug Window.
By temporarily changing the values of various settings and variable boxes, you can efficiently test play and check for progress and defects.
Any settings you specify in this window will not be reflected in the game until you press the "Reflect in Test Play" button.
- Change Settings Tab
Various temporary changes can be specified to facilitate test play.
- Options
- Disable Encounters
If checked, monsters will not be encountered.
- Pass Through Events
The player will be able to move through events.
Stairs and doors can also be slipped through, which may prevent the player from moving from one location to another.
- Always Max HP and MP in Battles
During battles, the HP and MP of the party casts are always at their maximum values.
- Max Abilities in Battles
During battles, the abilities of the party casts are always at their maximum value.
- Fast-Forward in Battles
If checked, battles that occur during test play will be executed in fast forward.
- Change Cast's Level
You can change the level of the cast currently in the party.
- Display/Edit Variable Boxes
Temporarily change the value of variable boxes.
Checked entries in the checkboxes are displayed at the top of the list.
- Close Button
Close the debug function dialog and return to test play.
- Reflect in Test Play Button
Reflect the changes in the test play.
Cast levels, event switches, and variable boxes are reflected only where values are entered.
- Logs Tab
This function allows you to monitor which events are being performed during test play.
If necessary, use the buttons at the top of the log to select the event type to be displayed.
If there is a type of event that repeats in parallel, a large volume of logs will continue to flow. In that case, please turn off "Include Parallel Events".
- Sources
In the Common Event log, the action that triggered the execution of the common event is displayed in the "Sources" field.
| Triggering Action | Displayed Content |
| Map Settings Palette > Basic tab > Event to be Called Before Displaying Map | Execute From Map |
| Skill Event | Execute From Skill |
| Item Event | Execute From Item |
| Layout Action | Execute From Layout |
| Event Panel "Specify Game Over" | Execute From GameOver Action |
- System Status Tab
Display the current status of various system flags as enabled or disabled.
You will be able to see the initial game specs as well as the state of the game as it has been changed through events.
- Event Monitor Tab
Display the status of the event being executed.
About the Cast Parameter Check View†
You can open and close the Cast Parameters View by pressing on the "F6 key" during test play.
You can check the statuses of party members, enemies in battle, and cast events on the map.
In addition to the cast member's own status, the status also shows the values changed by class, equipment, and various influences during the battle.
It is also possible to temporarily change the values of some statuses and information about the skills held by the casts.
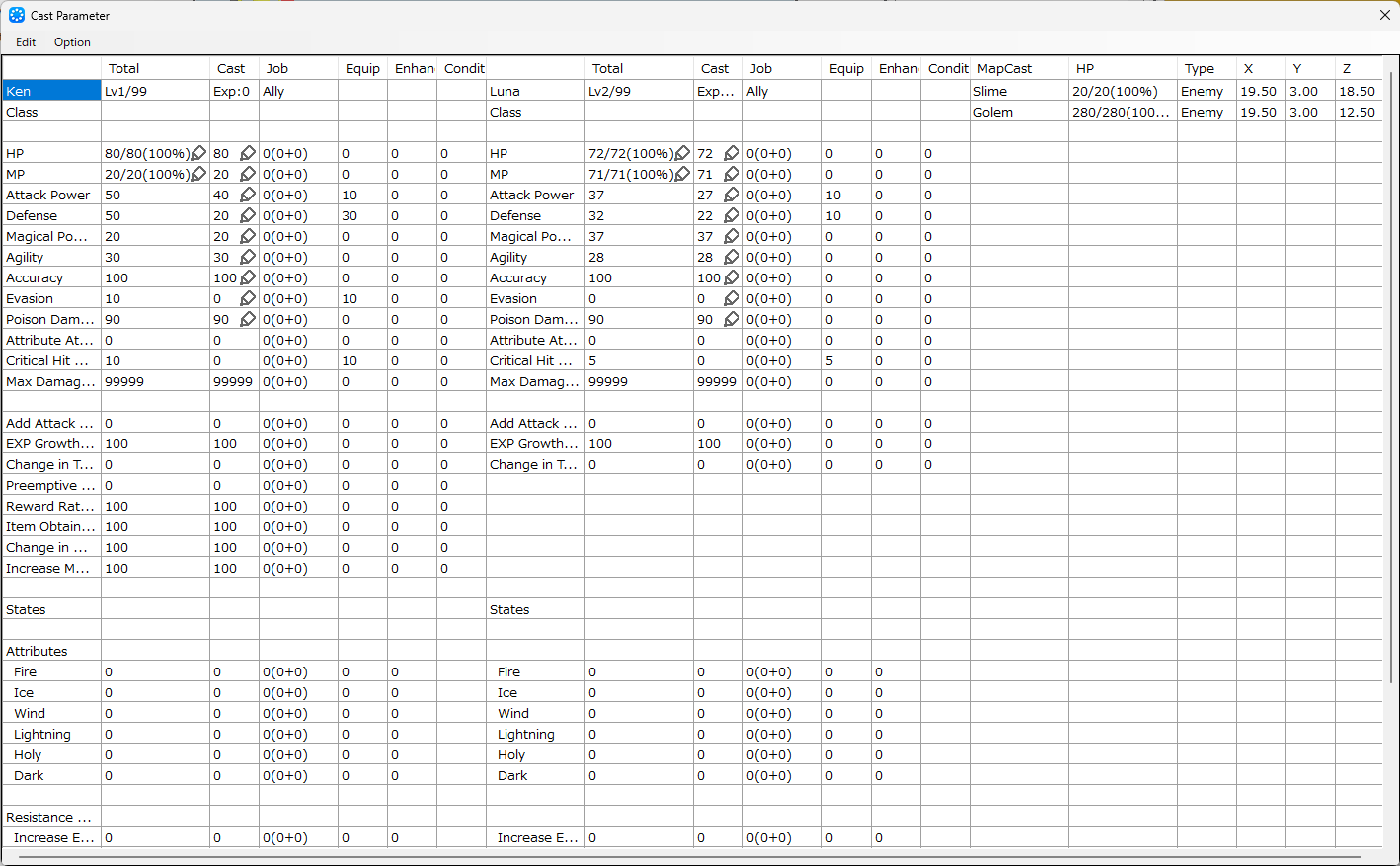
- Edit
An editor will open that allows you to change the skills available to the party members.
This function allows you to temporarily change the skills available to party members and information about the party's possessions.
- Skill
This opens an editor where you can change the skills available to the party members.
Select a cast and check the checkbox for each skill to use that skill.
- Item
An editor will open that allows you to change the amount of money and the number of items in the party's possession.
You can assign a number of possessions to increase or decrease, or discard items in their possession.
- Option
You can choose whether to display information about cast events on the map.
The display format can be selected to display all status of the cast events (Full) or only HP and location information (Simple).
Performance Meter†
Various graphs show how much load is being applied to rendering, logic processing, etc.
Placing many objects and events, or executing complex processing events simultaneously, increases the processing load and makes the game feel sluggish when played.
The Performance Meter is a feature that helps you adjust them.
(!)How much the processing load affects the operation depends on the environment being used.
- On
A simple graph showing CPU/GPU load and FPS is displayed.
- Time Series Graph
The load history of 300 frames is displayed in a graph.
The items are as follows:
- GPU
| Shdw | This is a shadow rendering. |
| ZPre Zprepass | This is a pass to avoid expensive fragment shader load by writing the depth first. |
| Base | This is a pass where the opaque elements are mainly written. |
| Rflct, Lgt, Gather, Gahter2 | They are not functioning currently. |
| SSS | This is a SSS rendering pass. |
| Unlit | This is a pass of the non-lighting material. |
| Fog | This is a fog rendering pass. |
| Trans | It is a translucent rendering (including particles). |
| Fxaa | It is an anti-aliased rendering. |
| SSAO | This is a SSAO rendering. |
| Dof | This is a depth-of-field pass. |
| Bloom | Bloom (including LUT vignettes and other pass that will eventually be dropped into the LDR) |
| UI | This is a UI rendering. |
| Other | Other debugging displays, etc. |
- CPU
| Update | Game processing update |
| GraphicsUpdate | Update model animations, etc. |
| Batch | Gathering rendering information |
| Rendering | Rendering API call |
- Other Value Information
| Resolution | Dynamic resolution adjustment state of Base and Shadow. If it is 100%, it is rendering at full resolution. Depending on the rendering load, Base may drop to 75% and Shadow to 50%. |
| Allocator | GFX: Allocator usage for class instances that are frequently created and deleted in graphics.
GLIST: List node allocator for connecting geometry and materials. |
- Details
Displays the instantaneous value of the previous frame by thread and by nest.
The colors on the graphs represent the same content as the time series graph.
For MainThread, GPU, the occupied time of one frame is shown in % based on 1/60 second.
Named graphs other than GPU are threads.
The unnamed graph is a nested section of function calls belonging to the named graph below it.
You can pause and select a section.
| Pause Key | Pause graph updates. |
| PageUp Key, PauseDown Key | When pressed while paused, it moves through the sections one by one, displaying the name of the section and the elapsed time. |
- Logic Load
Displays the Bakin engine load during test play execution.
Other information, such as the current camera direction, can be viewed.
The following processing times are shown for each.
- general
| total | The total time elapsed between the previous frame and the current frame. This includes time when the CPU is not processing, such as waiting for vertical synchronization. |
| update | Total time for the update section below. |
- update
| System | This is the time taken for basic engine processing, such as updating input information and window control. |
| Event | This is the time taken to process the event contents. |
| Character | This is the time taken to control the position and orientation of characters on the map. |
| Player | This is the time taken to accept the player's input and process the movement. |
| Battle | This is the time taken to process the battle. |
| Menu | This is the time taken to process the menu. |
| ETC | This is the time taken for other detailed processing (image coordinate management, wipe, camera control). |
Reset†
Reset the test play and return to the title screen. (If you skipped the title screen, it will take you back to the beginning of the game.)
Ctrl+c can also be used to reset.
This menu is not selectable during test play with center wheel click.
4) Status Bar†
The status bar at the bottom of the Map Editor window contains icons for frequently used functions.
- Selection Target
Narrow down the selection.
- Terrains Only
When turned on, only terrain is selected.
- Objects Only
When turned on, only objects and events are selected.
- Terrains and Objects
When turned on, both terrain and objects and events are selected.
In addition to the selection of different targets, the copy/cut/paste behavior in the map editor changes depending on the mode.
- "Terrains Only": Copy, cut, and paste selected terrains.
- "Objects Only": Copy, cut, and paste selected objects and events.
- "Terrains and Objects": Copy, cut, and paste selected terrains and the objects/events that will be placed on them.
- Operation Axis
Specify the axis of operation for moving objects and events.
- XZ
Only the X and Z axes are available for operation.
- YX
Only the Y and X axes are available for operation.
- ZY
Only the Z and Y axes are available for operation.
- Place on Top
When placing an object or event, place it so that it sits on top of what is already in place.
However, if the stamps to be placed do not have collision specified, they will not be placed on top, even if this button is turned on.
When placing while holding down the Ctrl key, the placement will stack on top of what has already been placed. (If this button is turned off, the opposite action will be performed.)
- Manipulator
Select the manipulator type.
- Position Adjustment
When turned on, the manipulators are used to adjust the position of objects and events.
- Angle Adjustment
When turned on, the manipulators are used to adjust the angle of objects and events.
- Scale Adjustment
When turned on, the manipulators are used to scale objects and events.
- Grids
- Snap to Grid
Enable/disable the Grid Snap function, which positions objects and events along grids.
- Show Grids
Show/hide the grids on the map.
- ON/OFF
- Camera from Above
When turned on, the camera will look at the viewpoint from directly above. Turn off to return to the previous viewpoint.
- Perspective View
Switch between having the map you are working on displayed with/without perspective.
- Post-Effects
Switch between applying or not applying the post-effects specified for the map you are working on.
- Map Symbols
Display/hide event markers and collisions without lights, particles, or graphic settings placed on maps.
- Enemy Distribution
When turned on, the color of the ground changes in areas where appearing enemies are specified in Map Settings > Enemy Distribution.
The entire map appears to change color when enemies are placed in ALL (Entire Map) in the range of Enemy Distribution.
If you think the color of the map is wrong, check the on/off state of this button and the Enemy Distribution setting.
- View Collision
Display/hide collision frames (white wireframes) for events placed on maps that do not have graphics specified.
Also, when this button is turned on, the collision frame of the underlying object will be displayed when an object is attempted to be placed on top of another object.
Note that if the Map Symbol button is off, collisions will not be displayed when this button is turned on.
- DOF
Enable/disable the DOF (depth of field) function.
If the Post Effects button is off, DOF is not enabled when this button is turned on.
Since DOF is a function of the camera position as the origin, the amount of DOF applied in the Map Editor is different from the amount of DOF applied in the game.
Please check the preview of the camera tool to see the correct DOF applied in the game.
5) Various Palettes†
The "palette" is a collection of functions for creating maps by type.
There are six palettes used in the Map Editor
For a description of the function of each palette, please refer to "Various Palettes used on the Edit Screen" in this help.
- Auto Hide
Clicking on the push-pin icon in the upper right corner of each palette will move the palette to the left or right side of the preview screen, allowing you to use the editor more spaciously.
Stored pallets are shown/hidden each time the pallet name in the left/right side storage section is clicked.
- Moving and Sizing Palettes
The palette can be moved to any desired location by left-dragging the title menu section.
To return to the original location, double-click on the title menu section.
The palette can also be resized by dragging the frame to the left.
![[PukiWiki] [PukiWiki]](./skin/BAKIN_logo_92.png)